
By LaurenMarie SEPTEMBER 28, 2007 – 9:00 AM
When you are working on a design, do you have to use the Tools Palette at all in Photoshop or have your fingers memorized the shortcuts?
Not using the Photoshop key commands is a sure way to slow yourself down; it’s frustrating to not be able to work as fast as your mind can think!
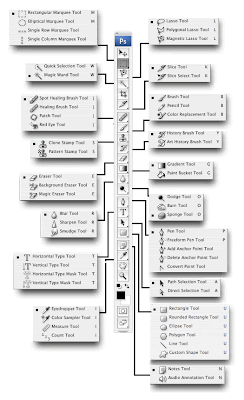
The Tools Palette
It is essential to learn the shortcuts for the tools you use most often. As I was writing this, it was very difficult for me to remember exactly which key I push to get these tools, my fingers just know what to do when my mind says “I need the _____ tool.” The following list is ordered the way they are on the Tools Palette: top to bottom, first the left column and then the right. The letter is the hotkey or shortcut, then I listed the tool name, other tools under the first one and then what the tools do.
• M=Marquee Tool, to make round, square or single row or column selections quickly
• L=Lasso Tool, also the Polygonal Lasso and Magnetic Lasso Tools, to make freehand selections, straight selections or selections that roughly go around the border of an object (best if the object is in high contrast to its background)
• C=Crop, to make the canvas of the image smaller or larger
• J=Healing Brush, to fix blotches, blemishes, scratches and other unwanted noise. Averages the color of the area being cloned and uses the texture of the target area
• S=Clone Stamp, also to fix unwanted noise, but this exactly clones the pixels from a target area
• E=Eraser Tool, use this tool sparingly because it complete deletes pixels. It is better to use a mask to hide unwanted areas of an image, because you never know when you’ll change your mind and want the whole thing back again!
• R=Blur Tool, also hidden under this tool are Smudge and Sharpen tools (you’ll rarely use Sharpen because it makes the image pixilated). The Blur Tool will give you a brush that blurs the pixels you “paint”
• A=Path Selection Tool (black arrow), also here is the Direct Selection Tool (white arrow). The black arrow will select an entire path for you to move around, white arrow will allow you to select specific anchor points on the path.
• P=Pen Tool, used to make paths and can be used in conjunction with the arrow tools above. It’s best to have previously selected the white arrow and then select the pen tool. That way, when you hit control (or command) you will have the features of the white arrow to move anchor points.
• N=Notes, I never use this tool, but here it is if you need the shortcut. Notes allow you to create tagged points on a document and you can either record audio or type the message.
• H=Hand Tool, most important tool next to the Move Tool, however, it’s best to not actually switch to this tool because it’s easily accessible when in most other tools by hitting the spacebar. Hold the spacebar down to toggle the hand tool and drag your image around. When you’re where you want to be, let up.
• V=Move Tool, allows you to select layers (objects) and move them around the canvas. This will probably be the tool you select most often so be sure to learn it!
• W=Magic Wand, similar to the lasso and marquee tools because it allows you to make selections.
• K=Slice Tool, is used for cutting up images for websites. You can cut up the images and then automatically save them all for web without having to go through and name each image.
• B=Brush, you’ll be using this quite often, too, but you’ll have to actually select it using B. The brush tool can be used for lots of stuff from actually painting, to hiding or revealing parts of a mask.
• Y=History Brush, honestly, I’ve never learned how to use this tool or the one under it, the Art History Tool. Have you learned to use it? Please explain it to us below!
• G=Gradient Tool, to create fades from one color (or transparency) to another. The default will be from foreground color to background color. You will usually need to configure the options for this tool each time you use it. A quick tip: if you click and hold shift while you drag, your gradient will be in perfect 45 (or 90) degree angles.
• O=Dodge/Burn Tools, the Sponge (saturation) Tool is also here. Dodge is used to lighten an area of an image and Burn will darken it. These terms are retained from photography darkrooms, where a photographer would reduce or increase the exposure of parts of the image during development.
• T=Text Tool, allows you to create new text boxes. You can either single click and start typing or draw a box for your text and type in that.
• U=Shape Tool, creates vector shapes. Default options are rectangle, rounded rectangle, ellipse, polygon line and custom shape. If you hold shift while in the rectangle, rounded rectangle, or ellipse tool you will get a perfect square or circle. The custom shape tool has many options for ornaments, stars, bursts, etc. You’ll find the various options up in the context sensitive toolbar on the top of the screen below the menus.
• I=Eyedropper Tool, allows you to select a color that you seen on screen. You can also toggle this tool from the Brush Tool (B) by pressing alt (option). One thing you may want to do is set the sample size of the Eyedropper to a 3x3 average, that way, you don’t have to select the exact pixel of the color you want, it takes a 3x3 square average sample. You can set this option when you have the Eyedropper Tool selected (not toggled). Go up to the context sensitive toolbar and find the Sample Size drop down menu. Change it from Point Sample (default) to 3 by 3 (or 5 by 5) Average.
• Z=Zoom Tool, this is another tool that you will use quite often, but like the Hand Tool, you don’t need to ever select it. It is available when you’re in most other tools by holding down the spacebar and control (command) keys for zooming in and the spacebar, control (command) and alt (option) keys to zoom out.
Shortcuts for Common Functions
This is a quick list of frequently used functions (should we call them FUFs?). There are shortcuts for almost every function in Photoshop, especially in CS2 and above, but these are the ones I find myself using the most.
• D Restore Default Colors (black foreground, white background)
• X Switch Foreground and Background colors, especially useful when painting or masking
• F Switch screen modes between window, full screen (not the same as maximize) with a grey background, and full screen with a black background (the menus on top are also gone in this view, giving you a little more screen real estate to work with)
• Ctrl+D Deselects the current selection
• Ctrl+Alt+I (CS2+) Image Size Dialog Box, in Photoshop CS and below, there is no shortcut set for this function, so you can set it yourself by going to the Edit menu and selecting Keyboard Shortcuts.
• Ctrl+Alt+C (CS2+) Canvas Size Dialog Box, also not set in CS and below.
• 0 through 9 Change opacity (of an art tool like the Brush Tool or, if you’re not in an art tool, it changes the selected layer’s opacity). 0 is 100%, 9 is 90%, etc. You can also press two numbers in rapid succession to get other opacities; pressing 1 and 5 quickly will get you 15% opacity.
• Ctrl+Alt+0 (that’s a zero) 100% Zoom of image size
• Ctrl+0 (also a zero) Image and document window as large as possible, but still fitting completely on screen
• Home jumps to the upper left corner of the canvas (useful when zoomed in close)
• End jumps to the lower right corner of the canvas
• Ctrl+Alt+Shift+N New Layer
• Ctrl+Shift+C Copy Merged, will copy everything from every visible layer within the selection.
One last helpful tip: while you have something selected, right click while in a selection tool (Marquee, Lasso, not Magic Wand) and a context sensitive menu allows you to quickly Select Inverse, Feather, Make a Work Path from Selection, and Transform Selection, among other useful options. The Magic Wand tool has different options.
And remember, you can always set your own shortcuts by going to the Edit menu and selecting Keyboard Shortcuts. The shortcuts are categorized by the menu the functions are in or the palette the tools are on.
